Defect Clustering In Software Testing
Defect clustering is a concept that has been widely discussed in the field of software testing. The idea behind defect clustering is that a small number of defects or errors in a software system are responsible for a large percentage of system failures. In this article, we will explore defect clustering, why it occurs, and how it can be identified and addressed.
What is Defect Clustering?
Defect clustering is a common phenomenon in software testing, and it refers to the tendency of a small number of defects or errors to cause a large percentage of system failures. In other words, some specific defects tend to cluster together and cause most problems in a software system. These defects can be related to a particular area or module of the system, or they can be spread across multiple areas.
Why Does Defect Clustering Occur?
There are several reasons why defect clustering occurs. One of the main reasons is that defects tend to be interdependent. When a defect is present in one area of the system, it can often lead to other defects in related areas. For example, a defect in the authentication module of a system could lead to issues in the authorization module, which could in turn lead to problems with access control.
Another reason why defect clustering occurs is that some areas of a software system are more critical than others. If a defect is present in a critical area, such as the payment processing module of an e-commerce application, it can have a much larger impact on the system's overall functionality than a defect in a less critical area.
Why is Defect Clustering Important?
Identifying defect clusters is important in software testing because it allows testers and developers to prioritize their efforts and focus on the most critical defects first. By fixing the defects that are part of a cluster, testers can often address multiple issues at once and reduce the overall number of system failures.
Defect clustering is also important because it can help identify areas of the software that are particularly susceptible to defects. For example, if a cluster of defects is identified in a particular part of the software, it may indicate that there are underlying design or coding issues that need to be addressed.
Identifying Defect Clusters:
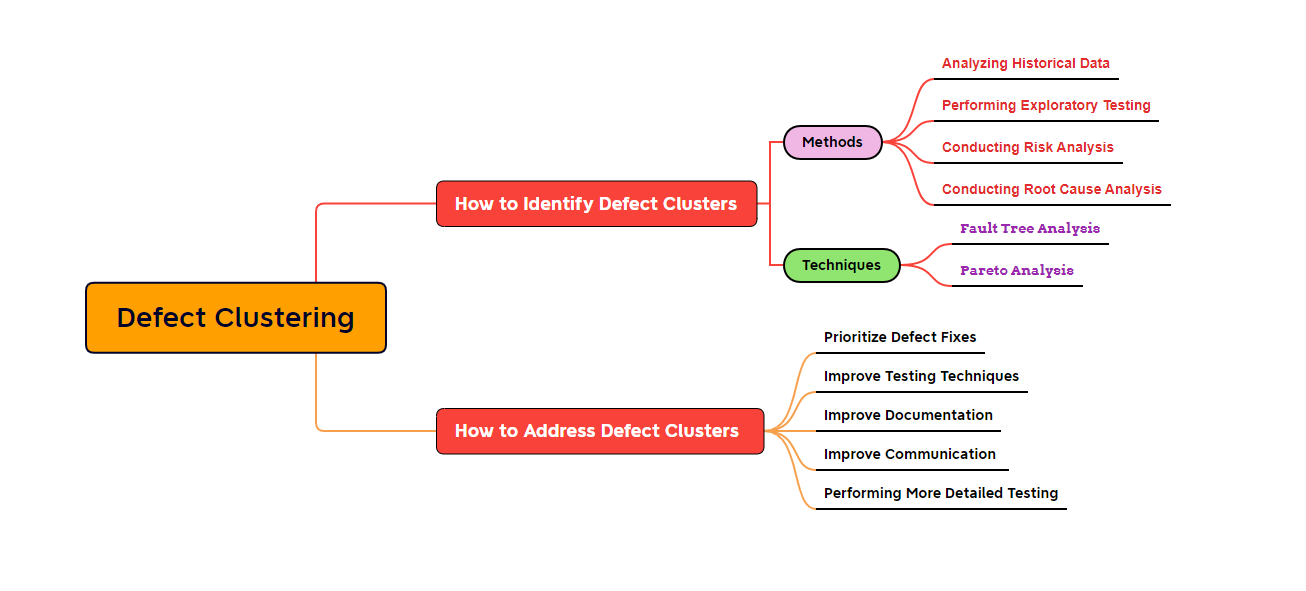
Identifying defect clusters requires a systematic approach to software testing and analysis. Some of the common methods used to identify defect clusters include:
Analyzing historical data: By analyzing data on system failures and defects, testers can identify patterns and clusters of defects that have occurred in the past.
Conducting exploratory testing: Exploratory testing involves ad hoc testing of the software to identify potential defects and areas of weakness.
Conducting risk analysis: Risk analysis involves identifying potential areas of risk in the software and prioritizing testing efforts accordingly.
Conducting root cause analysis: Root cause analysis involves identifying the underlying causes of system failures and defects.
Identifying defect clusters is an important part of software testing. By identifying clusters, testers can prioritize their efforts and focus on the most critical defects first. There are several techniques that can be used to identify defect clusters:
Fault Tree Analysis: Fault tree analysis is a technique that is used to analyze the causes of system failures. By constructing a fault tree, testers can identify the specific events or conditions that led to a particular failure. This can help to identify defect clusters, as it allows testers to trace the root cause of a failure back to the specific defects that caused it.
Pareto Analysis: Pareto analysis is a technique that is used to identify the most common or significant defects in a system. By analyzing defect data, testers can identify the defects that are responsible for the majority of system failures. These defects are the ones that are likely to be part of a defect cluster.
Addressing Defect Clusters:
Once defect clusters have been identified, it is important to address them to improve the software system's overall quality. There are several ways to address defect clusters:
Prioritize Defect Fixes: By prioritizing defect fixes based on the severity of the defects and their impact on the system, testers can focus their efforts on the most critical defects first. This can help to reduce the overall number of system failures.
Improve Testing Techniques: By improving testing techniques, testers can identify defects earlier in the development process, before they have a chance to cluster together and cause system failures. This can be achieved through the use of automated testing tools, continuous integration, and other techniques.
Conducting more thorough testing: Testers can conduct more thorough testing of the software to identify and address defects before they can cause system failures.
Improving documentation and communication: By improving documentation and communication, testers and developers can ensure that defects are identified and addressed more quickly and efficiently.
Conclusion:
Defect clustering is a common phenomenon in software testing, and it is important for testers to be able to identify and address it. By identifying defect clusters, testers can prioritize their efforts and focus on the most critical defects first. By addressing defect clusters, testers can improve the overall quality of the software system and reduce the number of system failures. With the right techniques and tools, defect clustering can be effectively managed and minimized in software systems.




We are a group of volunteers and opening a new scheme in our community. Your website provided us with valuable information to work on. You have done an impressive job and our whole community will be grateful to you. test automation
ReplyDelete